Subject: Rain Barrel LID Fluxes in SWMM 5.0.021
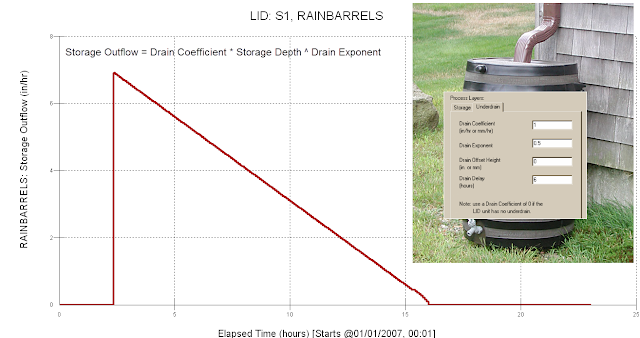
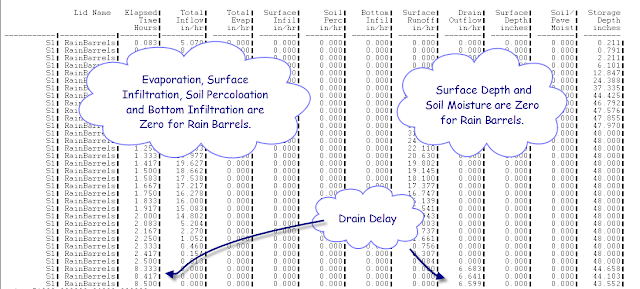
The fluxes are limited in a Rain Barrel Low Impact Development (LID) control in SWMM 5. The fluxes only include (Figure 1 and Figure 2):
1. Total Inflow,
2. Surface Outflow,
3. Drain Outflow and
4. Final Storage
The fluxes are also listed in the LID Performance Summary Table in the output text file.
***********************
LID Performance Summary
***********************
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Evap Infil Surface Drain Init. Final Pcnt.
Inflow Loss Loss Outflow Outflow Storage Storage Error
Subcatchment LID Control in in in in in in in
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
S1 RainBarrels 110.95 0.00 0.00 62.95 28.15 0.00 23.11 -2.94
|
Figure 1. Flux Pathways for a Rain Barrel LID |